Clean Energy Jobs in US Touch 3.5 Million in 2024: Report
In 2024, the number of clean energy jobs in the U.S. rose 2.8%
September 30, 2025
Follow Mercom India on WhatsApp for exclusive updates on clean energy news and insights
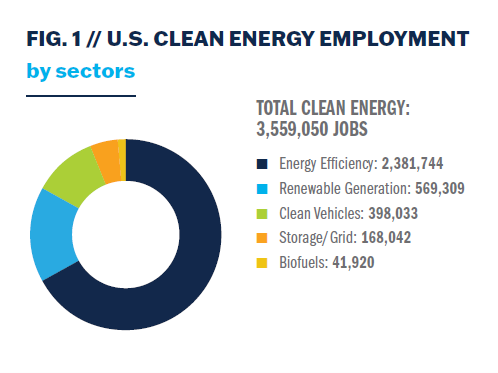
Over 3.5 million Americans were employed in clean energy occupations across renewable energy generation, battery and storage, energy efficiency, biofuels, grid modernization, and clean vehicle industries at the end of 2024, according to the Clean Jobs America report by E2.
Clean energy jobs grew 2.8% in 2024, adding nearly 95,697 new jobs, outpacing the rest of the U.S.’s employment rate by three times.
On a per-capita basis, clean energy jobs account for a significant share of the workforce nationwide, with an average of more than 2,200 jobs per 100,000 workers.
The clean energy sector accounted for 8% of all new energy jobs added in 2024.
It also accounted for 42% of nationwide employment in the energy and motor vehicle sectors.
Approximately 60% of all clean energy occupations, totaling 2.2 million jobs, are in the construction and manufacturing sectors. These include jobs involved in manufacturing solar components and building solar power projects.
According to the report, the South led clean energy job growth in 2024 with 41,000 new jobs, followed by the West and Northeast with over 22,000, and the Midwest with 4,000.
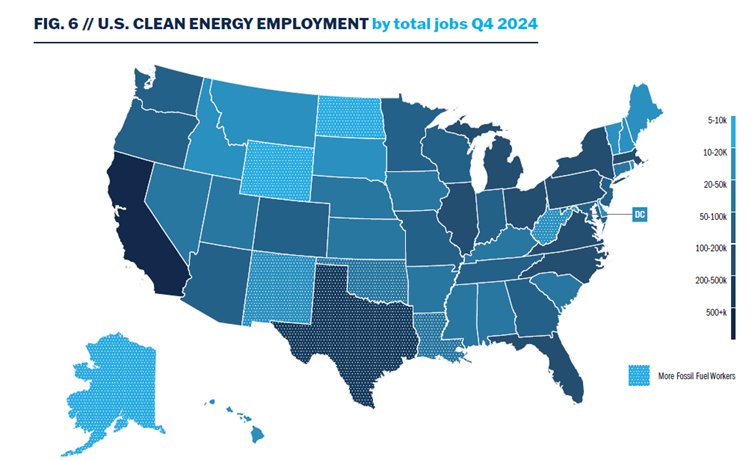
California led the nation with more than 550,000 clean energy workers, followed by Texas (281,000), Florida (184,000), and New York (180,000). Illinois, Michigan, Massachusetts, Ohio, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Virginia generated at least 100,000 clean energy jobs.
Solar and Wind
The solar sector led as the largest employer in the renewable energy generation sector with 370,000 jobs in 2024.
Onshore wind followed with nearly 132,000 jobs, concentrated in utility operations, construction, and supply chain.
Energy Storage
Among jobs in batteries, smart grids, and electric vehicle (EV) charging, clean storage technologies led with more than 93,000 jobs, followed by the smart grids sector with over 27,000 jobs.
At the start of 2025, the U.S. had added over 168,000 workers in the storage and grid sector.
Battery storage dominated clean storage employment, with nearly 79,000 workers, followed by 9,800 workers in pumped hydro storage.
On the grid side, apart from smart grids, microgrids led the job generation, totaling 21,500 jobs.
Battery storage alone supported more than 41,000 construction and 14,000 manufacturing jobs.
Employment in storage and grid modernization grew by over 23% by the end of 2024. Battery storage jobs expanded by over 20%, while EV charging employment shot up nearly 38% in just four years.
The country’s west and south were the largest employers in the storage and grid modernization sector, adding 55,900 and 55,600 jobs, respectively.
California and Texas lead in both clean storage and grid modernization jobs, reflecting large-scale integration of renewables and EV infrastructure.
Clean Vehicle Sector
The clean vehicle sector employed 400,000 workers across the electric, hybrid, and hydrogen vehicle sectors in 2024.
Hybrid EVs remained the largest segment in terms of job additions, with more than 161,000 jobs, followed closely by EVs at 148,000. Plug-in hybrids supported over 70,000 jobs, while hydrogen and fuel-cell vehicles employed more than 18,000 workers.
In the clean vehicle sector, the South (122,800 jobs) and the Midwest (122,200 jobs) lead in employment, followed by the West (100,000 jobs) and the Northeast (53,000 jobs).
Despite strong long-term growth since 2020, all regions experienced modest declines in 2024, with the Midwest experiencing the most significant drop (-4.6%).
California led with more than 70,000 jobs, supported by manufacturing and adoption incentives. Michigan, Ohio, and Tennessee also remained major hubs due to their existing auto industry supply chains.
Outlook
At the start of 2025, the clean energy sector was expected to remain the fastest-growing segment of the U.S. economy.
Jobs as wind turbine technicians and solar installers are projected to be among the fastest-growing occupations in the U.S., according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
However, it noted that recent policy changes surrounding the energy sector could put a strain on the continued growth of clean energy jobs in the U.S.
The report noted that, according to a separate research by E2, in the first half of 2025, companies canceled major clean energy-related factories and projects valued at more than $22 billion in the U.S. The policy changes also eliminated 16,500 previously announced jobs in the clean energy sector.
The same report by E2 also noted that the policy changes are placing U.S. workers and businesses at a competitive disadvantage in the global clean energy marketplace, which is on track to reach $2.2 trillion by 2025.
According to another report by E2, businesses in the U.S. have canceled or delayed over $14 billion in investments in clean energy and clean vehicle factories since January 2025, due to rising concerns surrounding the future of federal clean energy tax credits and policy.